
Do you want to get started with ESP8266? Then, read this post to figure out the best ESP8266 Wi-Fi Development Board for your project requirements.
The ESP8266 is a $4 (up to $10) Wi-Fi module. It allows you to control inputs and outputs as you would do with an Arduino, but it comes with Wi-Fi.
There’s a new board called ESP32, so you might like reading Best ESP32 Development Boards.
Comparing the ESP with other Wi-Fi solutions on the market, it is a great option for most “Internet of Things” projects! It’s easy to see why it’s so popular: it only costs a few dollars and can be integrated into advanced projects. Additionally, it is compatible with Arduino IDE. So, if you’ve worked with Arduino before, you’ll easily get used to working with the ESP8266.
We’ve published dozens of free ESP8266 projects and tutorials. One of the best projects to experiment with your ESP8266 when you’re getting started is building a simple web server to control outputs.
Recommended resource: Home Automation using ESP8266 eBook
Best ESP8266 Boards Comparison
At the moment, there are a wide variety of development boards with the ESP8266 chip that differ in the number of GPIOs, antenna styles, size, breadboard compatibility, etc…
We’ve created an in-depth ESP8266 Pinout reference guide covering exactly what each pin does and how to use them.
The best ESP8266 development board for your project will depend on what you intend to do. We’ll just cover a short selection of the most popular ESP8266 boards. The table below shows a quick comparison of the boards. Continue reading this post for a more in-depth analysis.
ESP-01 | ESP-12E NodeMCU | Wemos D1 Mini |
|
|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
|
Links | |||
GPIOs | |||
ADC Pins | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Flash Memory | 1MB (upgraded version) | 4MB | 4MB |
Breadboard-friendly | X | ✓ | ✓ |
USB to Serial Converter | X | ✓ | ✓ |
Size | 24.75mm x 14.5mm (0.97'' x 0.57'') | 48.55mm x 25.6mm (1.91'' x 1'') | 34.2mm x 25.6mm (1.35'' x 1'') |
Price | $ | $$ | $$ |
Recommended reading: ESP8266 Pinout Reference: Which GPIO pins should you use?
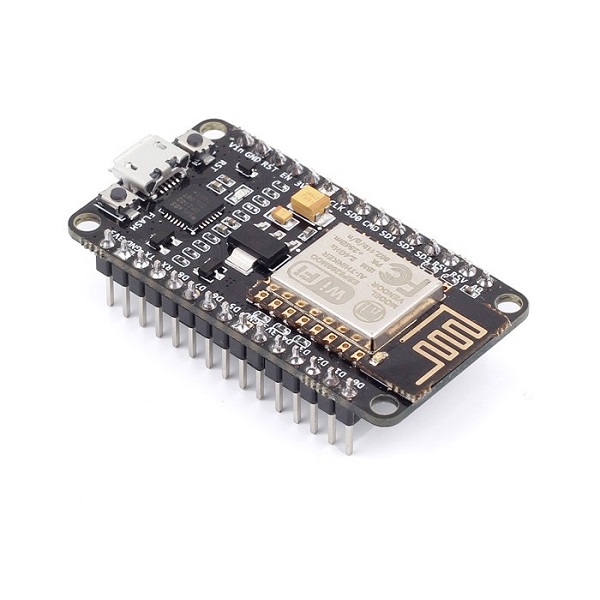
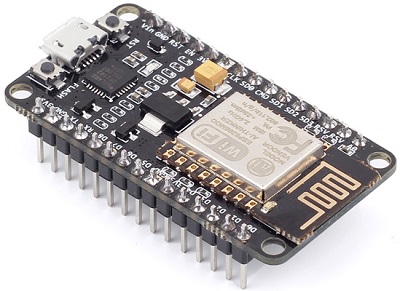
ESP8266 12-E NodeMCU Kit
The ESP12-E NodeMCU Kit is one of the most used ESP8266 development boards. It features 4MB of flash memory, access to 11 GPIO pins, and one analog-to-digital converter (ADC) pin with 10-bit resolution. In addition, the board has a built-in voltage regulator, and you can power up the module using the mini USB socket or the Vin pin.
Uploading code to the board is as easy as uploading code to the Arduino. There’s no need for an FTDI programmer, as it comes with a USB-to-serial converter built-in.
This is the ESP8266 board model we use more often in our Wi-Fi and IoT projects. It is very versatile, and it’s great for beginners. So, if this is your first time with the ESP8266, this module is a great choice. Take a look at the links below to find out the ESP8266 12-E NodeMCU kit on your favorite store.
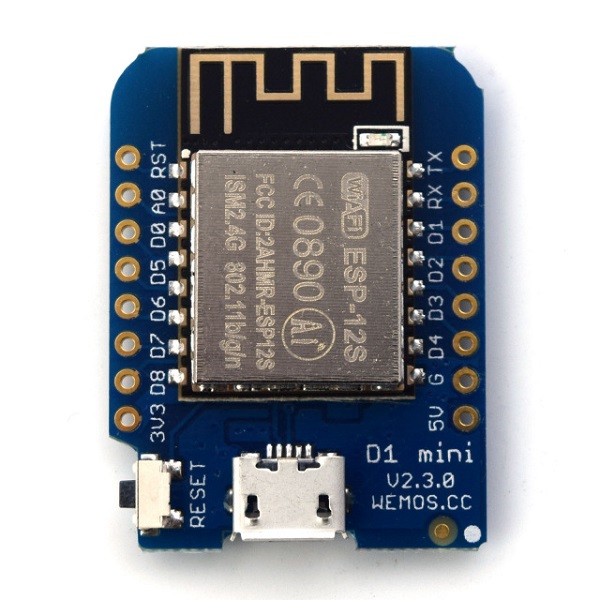
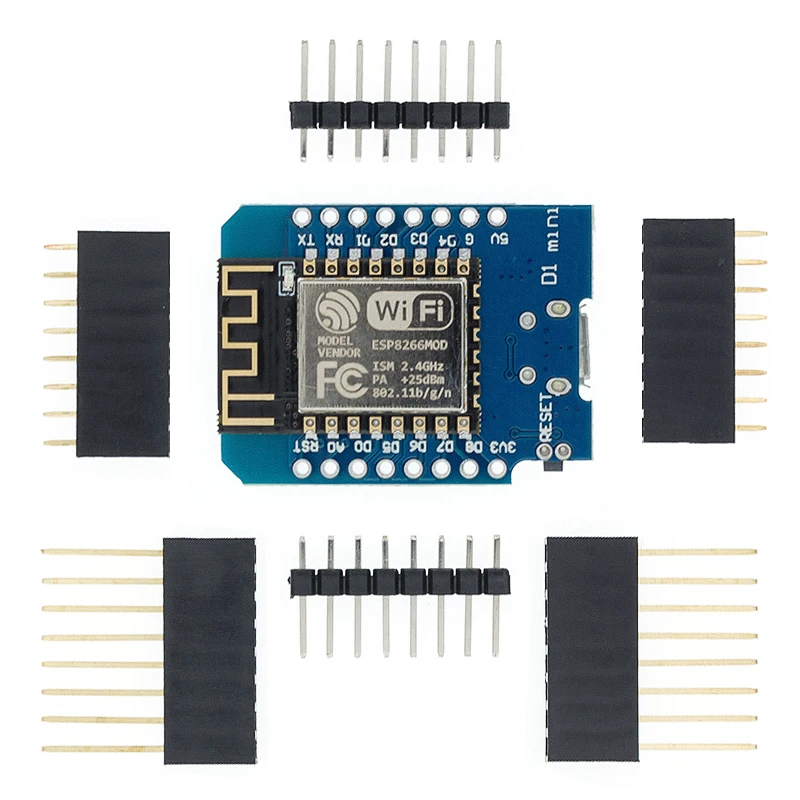
WeMos D1 Mini
The WeMos D1 Mini offers 4MB flash memory, 11GPIOs, 1 ADC pin in a minimal and small setup. So, if you need something that consumes less power for a more economical project, this is a good option. Additionally, the community has developed a wide variety of shields for the D1 mini board, which allows you to build small and simple setups with almost no wiring required. The WeMos D1 mini board is also a great option for beginners.
However, the board doesn’t come with the header pins soldered, so you need to solder them yourself. If you need a soldering iron, you can check the recommend soldering irons for beginners.
The WeMos D1 mini board costs around $4 depending on the store. Check the links below to find the board on your favorite store.
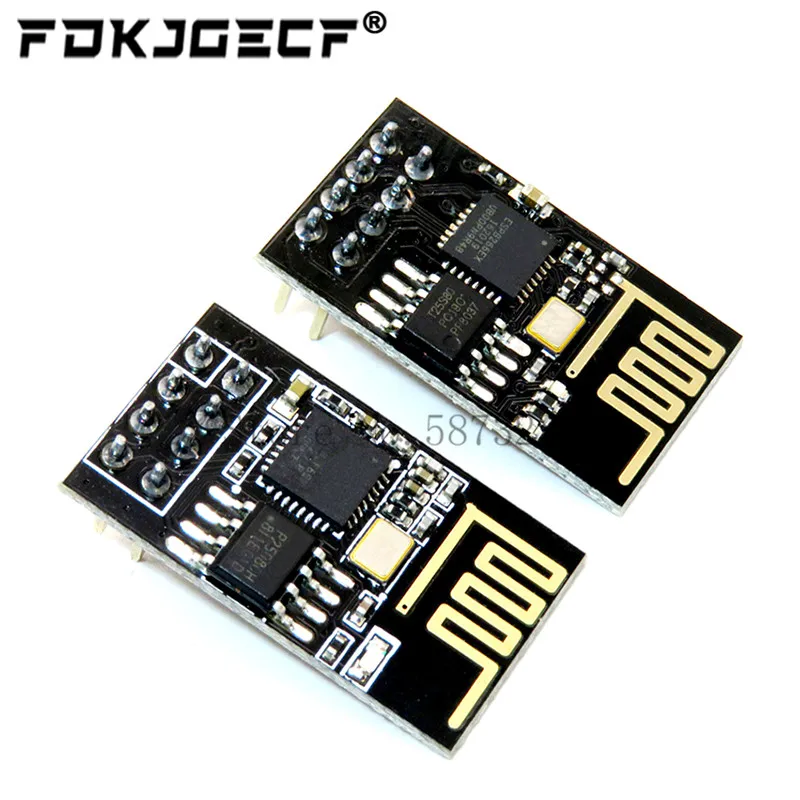
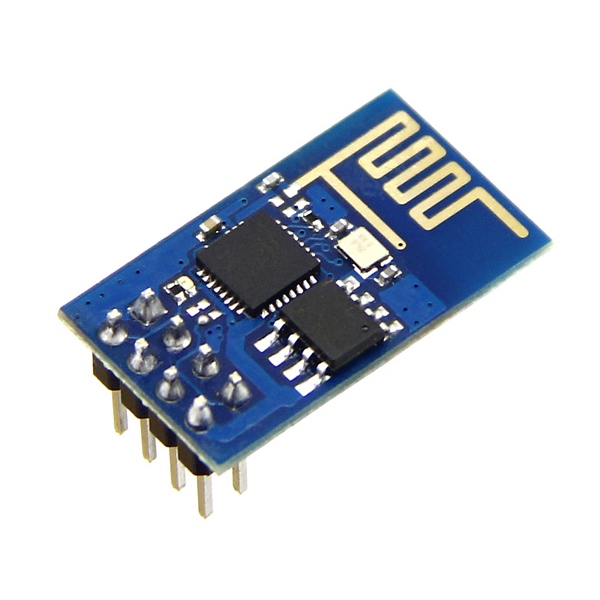
ESP8266 ESP-01
The ESP-01 is very small and fits in any enclosure, so it is perfect for finished projects. The upgraded version features 1MB flash memory (the previous version had 512 kB). In addition, it offers four GPIOs to control and connect peripherals (two of which are TX and RX for serial communication). So, if you need more peripherals in your projects, it is better to use one of the previous boards.
Unfortunately, the board doesn’t have a built-in voltage regulator, so you need to use a 3V3 power source or add a voltage regulator to drop the input voltage to 3V3. Additionally, it doesn’t come with a USB to serial converter, which means you need an FTDI programmer to upload code to the board. If you want to get started with the ESP-01, read our getting started guide.
The ESP-01 is great for applications that require a small number of peripherals. However, if this is your first time using the ESP8266, we recommend getting one of the previous boards. Those are more beginner-friendly and more versatile.
This is the cheapest ESP8266 module. Check the links below to find the ESP-01 on your favorite store.
Recommended resource: Home Automation using ESP8266 eBook
Need Help Getting Started with the ESP8266?
The ESP8266 made Wi-Fi and IoT projects more accessible to makers, hobbyists, and general public due to it’s great features, easiness to use, and affordable price. If you want to build your own IoT project, and need some help getting started, we have several resources for you.
Home Automation with the ESP8266
This is our premium ESP8266 course. Learn how to use your ESP8266 to automate your house. Even if you are an absolute beginner, you’ll be able to follow along and came up with your own IoT projects. You can get access to the course here.
ESP8266 Projects
We have dozens of free projects with the ESP8266. Here’s a short list of some of our most popular projects:
- ESP8266 Web Server
- ESP8266 DHT11/DHT22 Temperature and Humidity Web Server with Arduino IDE
- Voice Controlled Relay – Alexa with ESP8266
- ESP8266 Wi-Fi Button – DIY Amazon Dash Button Clone
- ESP8266 Remote Controlled Sockets
You can also search all our ESP8266 projects.
Wrapping Up
In this article, we’ve taken a look at three different ESP8266 development boards: ESP8266 12-E NodeMCU Kit, WeMos D1 Mini, and ESP-01. Of course, there are many more different boards available, but we reviewed the ones we use more often, which are also the most popular.
We recommend the NodeMCU Kit or the WeMos D1 Mini because both boards have a built-in programmer chip, making it easy to upload code. Additionally, they also offer a reasonable number of GPIO pins. If you are a beginner, you should go for one of these boards. However, if you need a tiny board for your project and only need 2 GPIOs, the ESP-01 is a better and cheaper alternative.
In this post, we’ve shown you and compared our favorite Best ESP8266 Wi-Fi Development Boards. These are perfect to use in your Internet of Things (IoT) projects. So which one is your favorite?
You might also like reading:
- ESP32 vs ESP8266 – Pros and Cons
- ESP32 Development Boards Review and Comparison
- ESP8266 Pinout Reference
Looking for more great deals on electronics and tools? Make sure you subscribe to catch upcoming deals and score some extra savings on your favorite gear!
[Recommended Course] Learn ESP32 with Arduino IDE
Register in our brand new ESP32 course with Arduino IDE. This is our complete guide to program the ESP32 with Arduino IDE, including projects, tips, and tricks! The registrations are open, so sign up now.



















 [eBook] Home Automation using ESP8266 »
[eBook] Home Automation using ESP8266 » [Course] Build a Home Automation System »
[Course] Build a Home Automation System » [Course] Arduino Step-by-Step Projects »
[Course] Arduino Step-by-Step Projects »
Leave a Reply